Design Technology
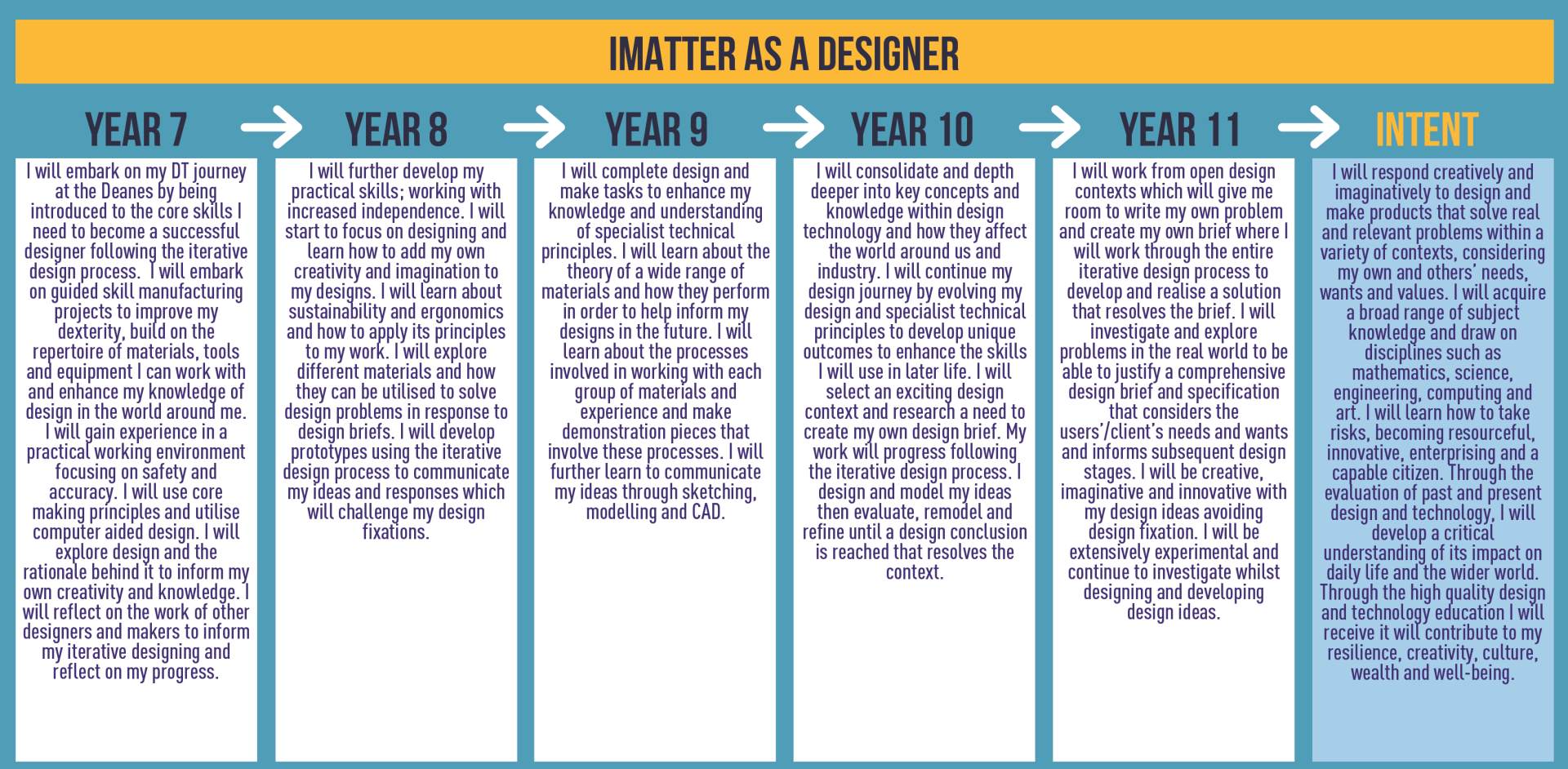
Year 7 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
Students will be learning a range of core skills needed within designing, making and evaluating as well as developing their technical knowledge. Some of the core skills include drawing techniques, working practically in the workshop and using CAD/CAM technologies. |
Students will gain an understanding for DT and the core skills involved to be able to design, make and evaluate effectively. Students will know how to analyse a brief and write a specification to allow them to evaluate the success of products. They will demonstrate a range of drawing techniques and select and use specialist tools and equipment to create products within the workshop and using CAD/CAM. | Students will be able to analyse and evaluate the success of products or their own work. They are able to draw in 3D using a range of techniques, using rendering skills to bring them to life. They will use safe, efficient and accurate working practices independently, following initial demonstration of the process. They will be able to explain the correct use of individual tools and will be able to demonstrate a sound understanding of the principles of design practices covered by the units work. | Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
|
Spring |
Students will be continuing to learn a range of core skills needed within designing, making and evaluating as well as developing their technical knowledge. Some of the core skills include drawing techniques, working practically in the workshop and using CAD/CAM technologies.In the later part of the term students will gain an understanding for what eco design is, how it affects everyday product design and know about ways to reduce the effect of design on the environment. |
Students will continue to gain an understanding for DT and the core skills involved to be able to design, make and evaluate effectively. Students will know how to analyse a brief and write a specification to allow them to evaluate the success of products. They will demonstrate a range of drawing techniques and select and use specialist tools and equipment to create products within the workshop and using CAD/CAM. Students will gain an understanding for eco design and how to reduce the impact on the environment through design. | Students will be able to analyse and evaluate the success of products or their own work. They will be able to draw in 3D using a range of techniques, using rendering skills to bring them to life. They will use safe, efficient and accurate working practises independently, following initial demonstration of the process. They will be able to explain the correct use of individual tools and will be able to demonstrate sound understanding of the principles of design practises covered by the terms work. | Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
|
Summer |
Students will be learning a range of core skills needed within designing, making and evaluating as well as developing their technical knowledge. Some of the core skills include drawing techniques, working practically in the workshop and using CAD/CAM technologies. |
Students will gain an understanding for DT and the core skills involved to be able to design, make and evaluate effectively. Students will know how to analyse a brief and write a specification to allow them to evaluate the success of products. They will demonstrate a range of drawing techniques and select and use specialist tools and equipment to create products within the workshop and using CAD/CAM. |
Students will be able to analyse and evaluate the success of products or their own work. They will be able to draw in 3D using a range of techniques, using rendering skills to bring them to life. They will use safe, efficient and accurate working practices independently, following initial demonstration of the process. They will be able to explain the correct use of individual tools and will be able to demonstrate sound understanding of the principles of design practices covered by the terms work. |
Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
Year 8 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
Through the iterative design process students will design and make a nightlight. Students continue to develop and build upon their core design technology skills. |
Students will learn and gain a practical knowledge of electronics and manufacture their own circuits. Students will study schematic and pictorial diagrams and be able to identify tools, equipment and components relevant to the electronics part of the unit. Students will analyse existing products and start to analyse a design brief, where they will identify a client and write their own design specifications. Students will develop their CAD skills to be able to use technologies to design and manufacture part of their nightlight. Students will prototype their designs to evaluate and modify them before realising and manufacturing their final design. | Students will use a guided iterative process to design creatively for their client. They will evaluate and develop their designs with an open-mind. Students will show resilience from set- backs and work hard to work through them. Students will have a sound knowledge of materials and manufacturing techniques and demonstrate confidence, independence and accuracy when working with them. | Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
|
Spring |
Through the iterative design process students will continue to design and make a nightlight. Students continue to develop and build upon their core design technology skills. |
Students will develop their CAD skills further to be able to use technologies to design and manufacture part of their nightlight. Students will prototype their designs to evaluate and modify them before realising and manufacturing their final design. Students will increase their knowledge and understanding for working with and selecting materials, tools, equipment and manufacturing processes. | Students will respond to the iterative design process creatively with the focus of designing for their client. They will evaluate and develop their designs with an open-mind. Students will show resilience from set- backs and work hard to work through them. Students will have a sound knowledge of materials and manufacturing techniques and demonstrate confidence, independence and accuracy when working with them. | Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
|
Spring |
Students learn about manufacturing techniques and safe working procedures in the workshop. They will learn how to select materials and manufacturing techniques appropriate to them and how finishing techniques can enhance the material or product. Students' knowledge will be embedded in how to analyse everyday products and identify their physical properties. Students will also learn how products are designed ergonomically and how to evaluate their effectiveness. |
Students will use their CAD skills to develop prototypes and to aid them in the manufacture of their salad server. Students will gain an understanding of how products are designed ergonomically and how they can use prototypes to test and evaluate their designs. Students will increase their knowledge and understanding further for working with and selecting materials, tools, equipment and manufacturing processes when appropriate. | Students will respond to the iterative design process creatively with the focus of designing for their client. They will evaluate and develop their designs with an open-mind. Students will show resilience from set- backs and work hard to work through them. Students will have a sound knowledge of materials and manufacturing techniques and demonstrate confidence, independence and accuracy when working with them. | Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
|
Summer |
Students will be building on the core skills they have learnt in designing, making and evaluating; along with their technical knowledge and apply them whilst working more independently through the iterative design process. The context in which they will be studying is British modern culture. |
Students will develop their skills further within the core skills needed in design technology in all areas. They will prototype their designs to evaluate and modify them before realising and manufacturing their final design. Students will increase their knowledge and understanding for working with and selecting materials, tools, equipment and manufacturing processes both by hand and using CAD/CAM. | Students will respond to the iterative design process creatively with the focus of designing for their client. They will evaluate and develop their designs with an open-mind. Students will show resilience from set- backs and work hard to work through them. Students will have a sound knowledge of materials and manufacturing techniques and demonstrate confidence, independence and accuracy when working with them. | Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
Year 9 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
Mechanical Toy (knowledge and designing) Students will study different types of movement focusing on the functions of mechanical devices to produce linear, rotary, reciprocating and oscillating movements. Students will explore changing magnitude and direction of force considering levels, linkages and rotary systems. Students will continue to embed their knowledge of the iterative design process to respond to a brief and to start designing their product to meet the needs of their client considering functionality, aesthetics and materials and manufacturing methods. |
Students will gain a knowledge of different types of movement and changing magnitude and direction of force considering levels, linkages and rotary systems. They will continue to embed their knowledge of how to respond to a brief and how to design considering the needs of their client considering functionality, aesthetics and materials and manufacturing methods. |
Students will respond to the iterative design process creatively with the focus of designing for their client. Students will have a sound knowledge of the types of movement and apply this in their designs. Students will demonstrate excellent communication skills with their well written design specification and design drawings. |
Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
|
Spring |
Students will continue to refine the core skills they have learnt in designing, making and evaluating; along with their technical knowledge and apply them working independently through the iterative design process. The context in which they will be studying is mechanisms and movement in children's toys. |
Students will develop their skills further within the core skills needed in design technology in all areas. They will prototype their designs to evaluate and modify them before realising and manufacturing their final design. Students will increase their knowledge and understanding for working with and selecting materials, tools, equipment and manufacturing processes both by hand and using CAD/CAM. |
Students will respond to the iterative design process creatively with the focus of designing for their client. They will evaluate and develop their designs with an open-mind. Students will show resilience from set- backs and work hard to work through them. Students will have a sound knowledge of materials and manufacturing techniques and demonstrate confidence, independence and accuracy when working with them. |
Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
|
Spring |
Pewter Casting: Through the iterative design process students will design and make a product. Students continue to develop and build upon their core design technology skills through analysing, designing, making and evaluating.
|
A design and make unit that students are given a context and are designing for others. CAD/ CAM is used to design and make moulds. Students get an opportunity to develop their manufacturing skills. Students will learn and expand their materials knowledge with metals and learn about manufacturing processes (casting and injection moulding) and how they link to scales of production. |
Students will respond to the iterative design process creatively with the focus of designing for their client. Students will have a sound knowledge of the materials they are working with and the manufacturing methods they are using; demonstrating safe and accurate making skills. They will also be able to explain advantages and disadvantages of different scales of production. Students will evaluate the success in their products by testing and comparing their work to their specification in detail. |
Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
|
Summer |
Pewter Casting: Through the iterative design process students will design and make a product. Students continue to develop and build upon their core design technology skills through analysing, designing, making and evaluating. |
A design and make unit that students are given a context and are designing for others. CAD/ CAM is used to design and make moulds. Students get an opportunity to develop their manufacturing skills. Students will learn and expand their materials knowledge with metals and learn about manufacturing processes (casting and injection moulding) and how they link to scales of production. |
Students will respond to the iterative design process creatively with the focus of designing for their client. Students will have a sound knowledge of the materials they are working with and the manufacturing methods they are using; demonstrating safe and accurate making skills. They will also be able to explain advantages and disadvantages of different scales of production. Students will evaluate the success in their products by testing and comparing their work to their specification in detail. |
Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
|
Summer |
Does It Connect Unit: Students will be broadening their knowledge on how to select appropriate manufacturing tools and equipment. They will learn the importance of accuracy and teamwork and how templates and jigs can be used to aid manufacturing.
|
Students will be applying their knowledge of tools, equipment and manufacturing processes to produce a product that will be ready for industry manufacture. They will gain an understanding on how products are produced accurately and consistently for batch products in industry and compare the main differences of using templates and jigs by hand or CAD/CAM. |
Students will respond to the iterative design process creatively with the focus of designing for their client. Students will be able to work well as a team to produce a product that demonstrates their knowledge of the materials they are working with and the manufacturing methods they are using to make an accurate industry standard product. They will also be able to explain advantages and disadvantages of different scales of production. Students will evaluate the success in their products effectively.
|
Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core design technology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. |
Year 10 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
Pupils will learn about the following topics: Industry, Enterprise, Sustainability, People and culture, society, environmental issues, production techniques and system. They will delve into energy generation and storage and about the development of new materials. Students will also learn about a variety of materials and their working properties and a range of manufacturing methods including the use of industry practices of producing products in batches;e.g. using jigs. |
Pupils will learn about the impact of new andemerging technologies including automation, and the use of robotics. Pupils will investigate businesses and start-ups looking at crowdfunding, virtual marketing and retail, co-operatives and fair trade. Pupils will look at the impact of resources both finite and non-finite as well as the disposal of waste. Pupils will be looking at new and emerging technologies and new waysof working driven by technological change. Pupils will learn about the positive and negative impacts new products have on the environment. Pupils will broaden and deepen their knowledge of materials and manufacturing processes. | Students will respond to the iterative design process creatively with the focus of designing for their client. Students will have a sound knowledge of the materials they are working with and the manufacturing methods they are using; demonstrating safe and accurate making skills. They will also be able to explain advantages and disadvantages of different scales of production. Students will evaluate the success in their products by testing and comparing their work to their specification in detail.Pupils will show the impact that modern materialshave on society. They will be able to show the impact in both positive andnegative ways and write a conclusion of their findings. Pupils should be able to show how the impact of modern technology will impact society and theenvironment and show an understanding of the main issues designers face whenusing modern materials. Students will produce a folding stool using a widerange of manufacturing process accurately and consistently to industrystandard. | Students work both practically and portfolio based will be assessed against an assessment criteria based on core designtechnology skills; designing, making, evaluating and technical subject knowledge. Students technical knowledge will be assessed in classwork books and online tests. |
|
Spring |
Students will be focused on the iterative design process and be given a context sustainability in our homes, from which they will identify their own problem and investigate it to be able to produce their own design brief and specification. Students will continue to embed their skills of generating design ideas and develop them and to realise those designs. Students will learn how to become confident in producing functional prototypes, both by hand and using CAD to be able to test and evaluate to further their designs. |
Students will be focused on the iterative design process and be given a context sustainability in our homes, from which they will identify their own problem and investigate it to be able to produce their own design brief and specification. Students will continue to embed their skills of generating design ideas and develop them and to realise those designs. Students will learn how to become confident in producing functional prototypes, both by hand and using CAD to be able to test and evaluate to further their designs. | Students will be creative, imaginative and innovative with their design ideas avoiding design fixation. They will be extensively experimental and continue to investigate whilst designing and developing design ideas. Students will consistently test and evaluate their functional prototypes to realise an innovative design. | Students will be covering A01, 2 and 3 of the assessment objects during this unit. Their portfolios will be assessed against each section of the assessment objective using the exam boards criteria for the NEA unit as they complete it; as they will be for their formal Non Examination Assessment (NEA) in year 11. The NEA unit as a whole makes up 50% of their final grade. |
|
Summer |
Students will be focused on the iterative design process and be given a context sustainability in our homes, from which they will identify their own problem and investigate it to be able to produce their own design brief and specification. Students will continue to embed their skills of generating design ideas and develop them and to realise those designs. Students will learn how to become confident in producing functional prototypes, both by hand and using CAD to be able to test and evaluate to further their designs. |
Students will work from an open design context which will give them room to write their own problem and create their own design brief where they will work through the entire iterative design process to develop and realise a solution that resolves their brief. They will investigate and explore problems in the real world to be able to justify a comprehensive design brief and specification that considers the users/clients needs and wants and informs subsequent design stages. | Students will be creative, imaginative and innovative with their design ideas avoiding design fixation. They will be extensively experimental and continue to investigate whilst designing and developing design ideas. Students will consistently test and evaluate their functional prototypes to realise an innovative design. | Students will be covering A01, 2 and 3 of the assessment objectives in the specification during this unit. Their portfolios will be assessed against each section of the assessment objective using the exam boards criteria for the NEA unit as they complete it; as they will be for their formal Non Examination Assessment (NEA) in year 11. The NEA unit as a whole makes up 50% of their final grade. |
Year 11 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
Students will be focused on the iterative design process and be working on their own design brief independently. |
Students will work from open design contexts which will give them room to write their own problem and create their own design brief where they will work through the entire iterative design process to develop and realise a solution that resolves the brief. They will investigate and explore problems in the real world to be able to justify a comprehensive design brief and specification that considers the users/clients needs and wants and informs subsequent design stages. | Students will be creative, imaginative and innovative with their design ideas avoiding design fixation. They will be extensively experimental and continue to investigate whilst designing and developing design ideas. Students will consistently test and evaluate their functional prototypes to realise an innovative design. | Students will be assessed on Sections A, B, C, D and F of their Non Examination Assessment (NEA) portfolio at the end of the Autumn term. The NEA unit as a whole makes up 50% of their final grade (with a total of 100 marks available in 6 sections). |
|
Spring |
Students will be focused on the iterative design process and be working on their own design brief independently. |
Students will work from open design contexts which will give them room to write their own problem and create their own design brief where they will work through the entire iterative design process to develop and realise a solution that resolves the brief. They will investigate and explore problems in the real world to be able to justify a comprehensive design brief and specification that considers the users/clients needs and wants and informs subsequent design stages. | Students will be creative, imaginative and innovative with their design ideas avoiding design fixation. They will be extensively experimental and continue to investigate whilst designing and developing design ideas. Students will consistently test and evaluate their functional prototypes to realise an innovative design. | Students will be assessed on the remaining sections in their Non Examination Assessment (NEA) portfolio (A-F) at the end of the Spring term. The NEA unit marks are sent off to exam boards at the end of the Spring term and makes up 50% of their final GCSE grade. |