Geography
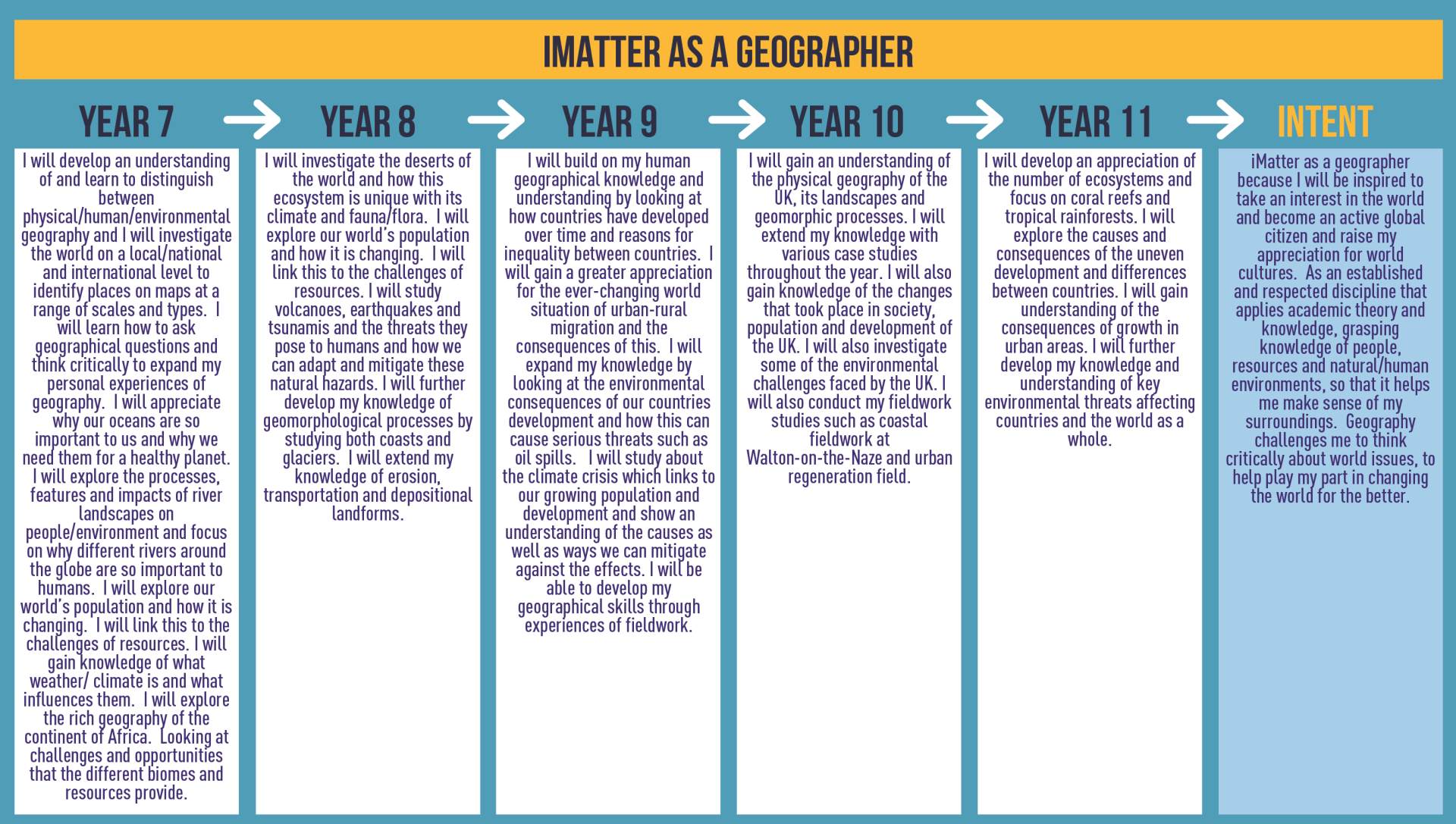
Year 7 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
What is a geographer |
Students will develop their locational knowledge by accurately locating countries, continents, and oceans. Students will expand their vocabulary of geographical terminology such as latitude and longitude. Students will develop their understanding of measuring distance, scales, grid references and symbols from OS maps. Students will also investigate how to use an atlas to quickly locate places using both the index and longitude and latitude. |
Students are adept at using maps at a range of scales. They can consider the advantages and disadvantages of different types of world map projections and decide which is the most accurate. Students demonstrate a range of skills when using an atlas and OS maps such as grid references, use of symbols, contour lines and latitude and longitude. |
Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed on their knowledge, understanding and enquiry skills through practical tasks. |
|
Autumn |
Oceans on the edge |
Students will expand their locational knowledge of the oceans and seas of the world. Students will investigate both the shallow and deep seas to see how fauna have adapted to survive and how the thermohaline circulation links all our oceans together. Students will investigate the threats to our oceans from humans such as climate change and oil spills while strategizing how best we can help our oceans to remain healthy. |
Students will be adept at locating a range of oceans and seas and understanding how our oceans are all connected through ocean currents. Students will be able to describe a range of adaptations and explain how these allow aquatic life to flourish in both the shallow and deep seas. Students will be able to analyse the threats facing our oceans and offer opinions and solutions to how we can manage these threats. |
Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed on their knowledge, understanding and enquiry skills through practical tasks. |
|
Spring |
How can rivers shape the land? |
Students will explore the physical processes of the water cycle and its interaction with land and sea. Students will gain knowledge of the different landforms and their formation processes on a river’s journey. In the lower course, we will look at meandering and channel changes into the estuary. Students will also assess how humans use the physical surroundings of the river for maximum gain for our societies but how this can be detrimental due to increased risk of flooding. | Students have a secure understanding of physical processes of the water cycle and river landforms. They are able to assess the uses of rivers from a recreational, industrial and economic point. Students will be able to explain the causes of flooding both human and physical and the effects floods can have along with how we can reduce the risk of flooding. | Formative assessment throughout involves prior knowledge memory retention starters. Prompt questioning in class for content clarification including direct questioning. A summative based assessment with multiple choice questions as well as extended writing questions about the processes of river landform creations and the social and economic uses of rivers. |
|
Spring |
Are there too many people on planet Earth? |
Students will gain an understanding of world population distribution and how the number of population changes. In this unit students will learn what factors affect population growth. Students will investigate the challenges of rapid population growth in parts of the world and attempts made by countries to reduce the growth. Students will also gain knowledge of how people use the Earth's natural resources such as water and oil and what problems of resource scarcity cause. | Students have a secure understanding of what is meant by population distribution and how the population of a country changes as it develops. Students can use a model to investigate population change, able to draw and interpret population data using population pyramids to predict change. Students have secure knowledge about how countries attempt population control and consider their successes. Students have a secure understanding of why it is important to maintain natural resources in a sustainable way. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks. |
|
Summer |
What should I know about the weather?
|
Students will gain knowledge on the difference between weather and climate and how we measure the weather to work out the climate of an area. Students will study the different types of rain and how air pressure and air masses give the UK such a unique weather system. Students will look at the factors that influence an area's climate such as altitude and distance from the ocean before finishing with a school microclimate investigation. This will introduce students to data collection and analysis to allow them to form conclusions based on their data and evaluate their methods. | Students will have a secure understanding of the difference between weather and climate and how we measure the weather. Students will gain knowledge on the factors that influence our weather and climate including the 3 types of rain, anticyclones and formation of depressions. Students will gain confidence in geographical fieldwork and how we use data to investigate and answer hypotheses. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks in a microclimate investigation. |
|
Summer |
Exploring Russia |
Students will gain an understanding of the location of Russia and how this location has influenced the country's climate, physical and human features and the population. Students will investigate what happened at Chernobyl and how this has impacted the surrounding ecosystems. Students will then investigate the ongoing crisis in Ukraine and the physical and human reasons behind this. Students will finish by investigating the resources available to Russia in the Arctic Ocean and gain knowledge and understanding on how these resources could benefit Russia economically but could come at a cost to the environment. |
Students will have a secure understanding of how Russia’s location has influenced its climate, population and human and physical features. Students will be able to describe and explain the impact that the Chernobyl nuclear explosion had on the surrounding ecosystems. Students will be able to articulate the reasons behind the war in Ukraine and how this could impact Russia’s future with other countries. Students will be able to evaluate the importance of the Arctic Ocean resources to improving Russia’s economy and whether the environmental damage is acceptable. |
Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students understanding of the subject.Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks. |
Year 8 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
Living in the desert |
Students will be introduced to the key features of deserts, the main characteristics of desert landscapes and how they are formed. Students will understand the reasons for adaptations. Students will identify how and why deserts might change in the future, consider how humans utilise and manage the landscape and the resources found within them. | Students can demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the defining characteristics of deserts. They can explain the factors that contribute to the formation of desert landscapes. Students can clearly articulate the reasons behind adaptations in desert organisms. They can provide detailed examples of specific adaptations and explain how these adaptations help organisms survive in the harsh desert environment. Students have an in-depth understanding behind the causes of desertification, the areas at risk and the impacts on people and the environment. | Formative assessment: Teachers use different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject.Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks which will assess their knowledge and understanding of landscapes formation and adaptations. |
|
Autumn |
Fieldwork Investigation |
Students will gain an understanding of how to design a geographical investigation to carry out around the school grounds. In this unit students will learn how to pose a hypothesis to answer, to design and collect primary data, present this data in a range of graphs, analyse the data and look for patterns, anomalies and to conclude by answering the hypothesis questions. Students will then give their opinion on the effectiveness of the study and its limitations and how it could be improved. Students will develop skills in questioning, analysing, data presentation, concluding and evaluating |
Students have a secure
understanding of what is need to conduct a geographical investigation .Students can explain the purpose behind conducting geographical investigations. Students have a secure understanding on how to collect, analyse and present data that they have collected and the role secondary data could have in supporting their findings. Students have gained the skill to interpret their data and reach an opinion on what is shows to conclude and answer their investigations question/hypothesis. |
Formative assessment: Teachers use different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks leading to a completed geographical investigation. |
|
Spring |
Will we ever know enough about earthquakes and volcanoes to live safely. |
Students will gain knowledge and understanding of physical geography and geology. Students will understand the lithosphere, internal structure and natural elements. They will be introduced to the natural phenomena of earthquakes, volcanoes and tsunamis; how they occur, what damage they cause, how humans mitigate the impacts and how they should respond. | Students can confidently apply concepts relating to tectonics. Students can use terms relating to different types of volcanoes, how they are created, what creates them and applying this knowledge to other natural phenomena. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students understanding of the subject.Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks. |
|
Summer |
Coasts |
Students will gain an understanding of coastal processes. Students will investigate how erosion, deposition and transportation create and change coastal landforms over time. Students then apply their knowledge to a specific UK case study at Jurassic coast. | Students can apply their knowledge from other natural processes e.g. rivers that directly link to coastal processes without thinking that there is a disconnect. Longshore drift, spit formation and the main geomorphic processes understood and explained confidently. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students understanding of the subject. Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks. Students will be tested on their knowledge and understanding of longshore drift, coastline processes and management strategies. |
|
Summer |
How does ice change the world |
Students will explore geographical processes in cold environments and how ice changes the world. Students will learn how erosion and deposition create glacial landforms. Students will identify glacial landforms on OS maps and explore how the distribution of ice around the world changes through time. Students will also investigate how people use glacial landforms. They will investigate glaciers and the impact of glaciation in the Lake District. | Students have a secure knowledge and understanding of how ice changes the world. Students can explain how erosion and deposition create glacial landforms; this can be difficult as these cannot be directly observed unlike rivers and coasts. Students can explain how each of the processes works by using keywords confidently. Students can identify glacial landforms on OS maps. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed on their knowledge and geographical understanding of concepts and glacial processes. Students will have to use OS map skills to identify glacial landforms. |
Year 9 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
What is Development and how can we make it more equal? |
In this unit students will tackle the concept of development and how it can be interpreted, measured and compared at a global scale. They will gain knowledge about how we come to see the world and the complexities of development as a constantly changing concept. The broader notion of quality of life is used throughout the unit so that the understanding of development is not focused on economic terms. Students are given a range of theoretical perspectives recognising multiple definitions of development. A range of factors will be used to explain inequalities operating at a range of scales. Development is a theme in the OCR GCSE curriculum. This unit is designed to give students an introduction to development which can then be further built upon at GCSE. | Students will progress their understanding and knowledge of global, regional and local scale to see how inequality exists in the world. Students can understand the concept of development and appreciate different definitions of development. They can understand that development occurs at different rates and times in different countries and identify reasons for poverty. They further develop understanding of the concept of sustainability, investigating sustainable development goals. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be completing a knowledge test, assessing their knowledge and understanding of the topic. They will also answer a series of enquiry questions and apply their knowledge and skills learnt throughout the unit. |
|
Autumn |
Should Brazil exploit the rainforest?
|
Students will be introduced to the case study of Brazil. Students will study the location, climate and unique animal and plant adaptations that make the rainforest so unique. Students will consider the goods and services that the rainforest can provide to indigenous people and people around the world. Students will then conclude if Brazil should use the rainforest resources to further their economy or whether the environmental damage is too great and instead conservation should be concentrated on for eco-tourism. |
Students will progress their understanding and knowledge of global, regional and local scale to see how inequality exists in the world. Students will be able to outline why the rainforests are important not just to Brazil but to the whole world. Students will be able to give their opinion on what Brazil should do with their rainforest whether that be deforestation to increase their economy or conservation to protect rainforest and promote sustainability. |
Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be completing a knowledge test, assessing their knowledge and understanding of the topic. They will also answer a series of enquiry questions and apply their knowledge and skills learnt throughout the unit. |
|
Spring |
What are the environmental consequences of development? |
Students will gain understanding of the current major resources of global energy, their sources, their extraction and how this is continuing at a solid rate into the future. Students will further develop their knowledge on renewables and fossil fuels. A major area of focus is the future and the potential take- over of renewables and slow reduction of fossil fuel consumption. Students will look into a focus region of the world where huge amounts of energy is consumed on a daily basis in order to operate and grow at an optimum rate (China). This will be explored deeper in understanding why they have gone about economic and industrial growth the way they have, as well as the consequences and damage to people and the environment. | Being able to bring in all concepts from pre-requisite topics and apply anything relevant to new concepts within this topic e.g. the exploitation of wood, using learnt content from deforestation in Brazil. Being able to fully comprehend the effects of every resource usage and all the damaging effects, as well as appreciating ways these can be mitigated and reversed in very eloquent language. Students are able to assess the effectivity of all energy sources and their relevance to the present day in terms of cost effectivity and optimum energy supply. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students understanding of the subject. Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks. |
|
Spring |
Urban world - Is the human jungle becoming the world’s biggest ecosystem? |
The ‘Urban World’ scheme of work focuses first on broadening pupils’ knowledge of where population is situated across the globe whilst establishing an understanding of why population is distributed in this manner. It then explores where in the World population is situated, with a focus on the process of urbanisation and the challenges and opportunities this can bring to both cities in higher income countries (HICs) as well as lower income countries (LICs) / newly emerging economies (NEEs). Whilst exploring these issues facing the urban world, students are constantly refining their understanding of sustainable development and conceptualising its applicability to city environments in HICs and LICs/NEEs, whilst judging the extent to which different places can be considered successful in their approaches to sustainability. With a focus on London and Lagos, the concepts, knowledge and skills covered within this scheme of work underpins further study of the issues facing the urban world addressed at KS4. The topic also helps to link knowledge that students have developed about Population, International Development and Globalisation topics to help them to think about how cities are constantly growing and changing to meet the demands of the ever-changing populations around the world |
Students will be able to deeply appreciate the cultural backgrounds and perspectives of all the countries and peoples covered to be able to assess and question lifestyle and reasons or making life choices based upon their priorities which will not exactly align with ours. |
Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students understanding of the subject. Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks. |
|
Summer |
Can we deal with the consequences of climate change? |
Students will gain an understanding of the natural causes of climate change and how this is different to global warming. Students will learn about the short- and long-term evidence of climate change and draw conclusions over which piece is the most convincing that climate change is real. Students will develop their skills interpreting maps and looking at the case study of how Tuvalu is being impacted by climate change. Students will investigate what we could do to manage climate change. |
Students have a secure understanding of the natural causes of climate change and global warming. Students can evaluate the short- and long-term evidence for climate to conclude whether it is real or not. Students have secure knowledge of the methods that are being developed to manage climate change. |
Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks. |
|
Summer |
Fieldwork enquiry: What should be done to reduce the risk of flooding on Canvey Island? |
In this unit students will have an opportunity to study their local area. Students will use a range of fieldwork techniques to investigate their enquiry question. Students will design their fieldwork techniques and use them to collect data. They will then present and analyse their data. Students will learn how to evaluate and reflect their experience during their fieldwork. | Students can design fieldwork techniques to use them to collect data. Students can present their data in different ways and be able to interpret their findings. They can look at trends in graphs or spot unusual results. | Students will be completing a combination of knowledge tests and extended writing tasks. They are designed to revisit skills and assess their knowledge and understanding. Successful completion of coursework of the investigation to be assessed. |
Year 10 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
Landscapes of the UK |
In this unit students will focus on developing their understanding of the physical landscapes found within the United Kingdom. This theme gives learners an understanding of the physical geography of the UK, its key landscapes and the geomorphic processes which have driven the changes to UK landscapes. Case studies will be used to contextualise how climate, geology and human activity work in combination with geomorphic processes to shape two landscapes in the UK. Students will develop skills in analysing and interpreting geographical data related to UK landscapes. | Students have detailed knowledge and understanding of geomorphic processes operating at different scales and how they are influenced by geology and climate. Students can apply their knowledge to explain the formation of landforms and identify features beyond case study locations. They can evaluate the impact of human activity and how it works in combination with geomorphic processes to shape the landscape. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed through exam style questions. |
|
Autumn |
People of the UK |
In this unit students will focus on developing their understanding of the human geography of the United Kingdom. This theme will develop an appreciation of the changes within the UK's society, its population and development. Students will learn about population distribution and density in the UK. They will gain knowledge of the diverse social and cultural characteristics within the UK. Case studies will be used to investigate the growth and/or decline of a place or region and to examine the character of a city in the UK, including the ways of life of the people who live in it.Students will study urban issues such as housing, transportation, sustainability and social inequalities within urban environments. | Students have a detailed knowledge and understanding of the UK’s diversity. Students display a deep knowledge of population distribution in the UK.Students have an understanding of the causes and the effects of, and responses to the ageing population. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed through exam style questions. |
|
Spring |
UK Environmental Challenges |
This theme provides students with a number of opportunities to engage with Geographical Skills and provides opportunities for local/UK fieldwork. Students will investigate the UK’s unique climate and hoe they can create extreme weather conditions. Students will gain an overview of how environments and ecosystems in the UK are used and modified by humans. They will gain understanding of energy supply in the UK and how it is affected by a number of factors. | Students can explain how air masses can cause extreme weather conditions in the UK. They have a clear knowledge and understanding of a UK flood event and they can explain the causes/effects of the flood as well as how they are managed. They can provide a clear explanation on how environments and ecosystems in the UK are used and modified by humans. They can justify reasons why non-renewable energy should contribute to the UK’s future energy supply. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed on their knowledge and understanding through exam-style questions. |
|
Summer |
Ecosystems of the Planet |
Students will investigate a variety of ecosystems that are spread across the world. Students will identify that these ecosystems have a number of interacting components and characteristics. Students will focus on key studies on coral reefs (Andros Barrier) and tropical rainforests (Peruvian Amazon). Learners will examine both ecosystems in terms of their abiotic and biotic components, processes, cycles, their value to humans and how we can mitigate threats through sustainable management. | Students will have a secure understanding of the components of ecosystems. They have knowledge of the climate, plants and animals within different ecosystems. They will identify the location of tropical rainforests and warm water coral reefs. They have a secure knowledge and understanding of the processes that operate within tropical rainforests and coral reefs including nutrient and water cycles. Students can explain the value, threats to biodiversity and attempts to mitigate threats through sustainable management within tropical rainforests and coral reefs. Students will increasingly make connections between units of study, understanding the interactions between human and physical processes and applying understanding in unfamiliar contexts. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed on their skills, knowledge and understanding through a series of exam-style questions. |
|
Summer |
Fieldwork preparation |
In this unit, students will have the opportunity to recap key areas in fieldwork investigation, from methodology and data collection to presentation and analysis. Students will be learning, practising and executing specific fieldwork techniques in order to be fully prepared for the fieldwork excursion. | Students will have a secure understanding of the process of a whole investigation, from hypothesis to conclusion. Students will meticulously collect data in the field as honestly as possible, create high quality data presentations using raw data, analyse the results respecting reliability and accuracy, interpret and conclude, linking back to the hypotheses. Students will advise on the future and possible follow-up investigations from the conclusions. | Students will be assessed on their on-going investigative work through formative questioning at every stage. A coursework-style approach will be used to assess students knowledge and understanding. |
Year 11 Curriculum plans
| Term | What are we learning? | What Knowledge, Understanding and Skills will we gain? | What will excellence look like? | How will these be assessed? |
|
Autumn |
Ecosystems of the Planet |
Students will investigate a variety of ecosystems that are spread across the world. Students will identify that these ecosystems have a number of interacting components and characteristics. Students will focus on key studies on coral reefs (Andros Barrier) and tropical rainforests (Peruvian Amazon). Learners will examine both ecosystems in terms of their abiotic and biotic components, processes, cycles, their value to humans and how we can mitigate threats through sustainable management. | Students will have a secure understanding of the components of ecosystems. They have knowledge of the climate, plants and animals within different ecosystems. They will identify the location of tropical rainforests and warm water coral reefs. They have a secure knowledge and understanding of the processes that operate within tropical rainforests and coral reefs including nutrient and water cycles. Students can explain the value, threats to biodiversity and attempts to mitigate threats through sustainable management within tropical rainforests and coral reefs. Students can engage in critical thinking by evaluating the effectiveness of sustainable management strategies for coral reefs and tropical rainforests. Students will increasingly make connections between units of study, understanding the interactions between human and physical processes and applying understanding in unfamiliar contexts. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed on their skills, knowledge and understanding through a series of exam-style questions. |
|
Autumn |
People of the Planet |
Students will investigate the social, economic and environmental definitions of development.Students will gain knowledge of various development indicators used to measure and compare the levels of development between countries. They will investigate the reasons for uneven development and different types of aid. Students will use case studies of one LIDC and EDC countries and will illustrate their economical development. Students will learn about the causes and consequences of urbanisation and how urban growth rates vary in parts of the world. | Students can identify reasons for uneven development and how different types of aid can be helpful and not helpful. They will demonstrate the ability to analyse the factors contributing to uneven development. They know the causes of rapid urbanisation and its consequences. Students will engage in in-depth case studies of LIDC and one EDC countries. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students' understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed on their skills, knowledge and understanding through a series of exam-style questions. |
|
Spring |
Environmental Threats to our Planet |
Students will learn about the causes of climate change and extreme weather conditions that cause many threats to both people and the environment. Students will gain knowledge of the consequences of climate change and how the global circulation of the atmosphere leads to extreme weather conditions in different parts of the world. Students will gain an understanding of key environmental threats that affect countries and the world as a whole. Students will study in detail about tropical storms and drought and investigate a case study of ‘The Big Dry’ in Australia, a drought event caused by El Nino/La Nina. | Students are aware of how climate has changed over time. Students have secure knowledge of the causes of climate change and how human activity is responsible for the enhanced greenhouse effect which contributes to global warming. They know a range of consequences of climate change and causes of the extreme weather conditions that are associated with the hazards of tropical storms and drought. Students have a secure understanding of how the extreme weather conditions of El Nino/La Nina develop and can lead to drought. They will be able to explain the effects of the drought event on people, ways in which people have adapted to drought and effects on the environment. Students will independently make connections between units of study, applying understanding in unfamiliar contexts and predicting global futures. | Formative assessment: Teacher uses different strategies during discussion and tasks to assess students understanding of the subject. Students will be assessed on their knowledge and understanding through exam-style questions. |